ACM模式
输入输出练习场:
〇、常识
-
LinkedList、HashSet、TreeMap、Arrays等 :均属于java.util包,需显式导入。 -
String、Math、System等 :属于java.lang包,无需导入 -
可以通过
import java.util.*;一次性导入java.util包中的所有类import java.util.LinkedList
import java.util.HashMap
import java.util.ArrayList
import java.util.Arrays
//一次性导入
import java.util.*; -
Integer.parseInt()和Integer.valueOf()的主要区别?**
Integer.parseInt(String s)会返回一个Int类型,但是Integer.valueOf(String s)**会返回一个Integer类型
Java中有基本类型和包装类型的自动转换,成为自动装箱和拆箱,以下是对照的表格
| 基本类型 | 包装类 | 自动装箱示例 | 自动拆箱示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
byte | Byte | Byte b = 100; | byte b = new Byte((byte)100); |
short | Short | Short s = 200; | short s = new Short((short)200); |
int | Integer | Integer i = 300; | int i = new Integer(300); |
long | Long | Long l = 400L; | long l = new Long(400L); |
float | Float | Float f = 3.14f; | float f = new Float(3.14f); |
double | Double | Double d = 2.718; | double d = new Double(2.718); |
char | Character | Character c = 'A'; | char c = new Character('A'); |
boolean | Boolean | Boolean bool = true; | boolean bool = new Boolean(true); |
一、字符串
1. String的基本特性
String是Java中的引用类型,一旦创建,内容不可变(immutable)。String对象存储在字符串常量池中,相同内容的字符串会共享同一个对象。
// 两种创建方式
String s1 = "hello"; // 字面量方式,直接在常量池中创建
String s2 = new String("hello"); // 使用构造函数,在堆中创建对象
2. 常用API
2.1 长度和访问
-
length(): 获取字符串长度
String str = "Hello";
int len = str.length(); // 返回5 -
charAt(int index): 获取指定索引位置的字符
String str = "Hello";
char ch = str.charAt(2); // 返回'l' -
toCharArray(): 将字符串转换为字符数组
String str = "Hello";
char[] chars = str.toCharArray(); // 返回{'H','e','l','l','o'}
2.2 查找和判断
-
indexOf(String str): 查找子字符串第一次出现的位置
String str = "Hello world";
int index = str.indexOf("world"); // 返回6 -
indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): 从指定位置开始查找
String str = "Hello world Hello";
int index = str.indexOf("Hello", 2); // 返回12 -
lastIndexOf(String str): 查找子字符串最后一次出现的位置
String str = "Hello world Hello";
int index = str.lastIndexOf("Hello"); // 返回12 -
contains(CharSequence s): 判断是否包含指定字符序列
String str = "Hello world";
boolean contains = str.contains("world"); // 返回true -
startsWith(String prefix): 判断是否以指定前缀开始
String str = "Hello world";
boolean starts = str.startsWith("Hello"); // 返回true -
endsWith(String suffix): 判断是否以指定后缀结束
String str = "Hello world";
boolean ends = str.endsWith("world"); // 返回true -
isEmpty(): 判断字符串是否为空
String str = "";
boolean empty = str.isEmpty(); // 返回true -
isBlank() (Java 11+): 判断字符串是否为空或仅包含空白字符
String str = " \t ";
boolean blank = str.isBlank(); // 返回true
2.3 字符串比较
-
equals(Object obj): 比较字符串内容是否相等
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
boolean equal = s1.equals(s2); // 返回true -
equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString): 忽略大小写比较
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = "hello";
boolean equal = s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2); // 返回true -
compareTo(String anotherString): 按字典顺序比较两个字符串
String s1 = "apple";
String s2 = "banana";
int result = s1.compareTo(s2); // 返回负数,表示s1在s2之前
2.4 字符串截取和分割
-
substring(int beginIndex): 截取从指定索引到结尾的子字符串
String str = "Hello world";
String sub = str.substring(6); // 返回"world" -
substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex): 截取指定范围的子字符串,左闭右开
String str = "Hello world";
String sub = str.substring(0, 5); // 返回"Hello" -
split(String regex): 使用正则表达式分割字符串
String str = "apple,banana,orange";
String[] fruits = str.split(","); // 返回["apple", "banana", "orange"] -
split(String regex, int limit): 限制分割次数
String str = "apple,banana,orange,grape";
String[] fruits = str.split(",", 3); // 返回["apple", "banana", "orange,grape"]
2.5 字符串修改
-
replace(char oldChar, char newChar): 替换所有指定字符
String str = "Hello";
String newStr = str.replace('l', 'L'); // 返回"HeLLo" -
replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement): 替换所有指定子字符串
String str = "Hello world";
String newStr = str.replace("world", "Java"); // 返回"Hello Java" -
replaceAll(String regex, String replacement): 使用正则表达式替换
String str = "Hello123World456";
String newStr = str.replaceAll("\\d+", ""); // 返回"HelloWorld" -
toLowerCase(): 转换为小写
String str = "HELLO";
String lower = str.toLowerCase(); // 返回"hello" -
toUpperCase(): 转换为大写
String str = "hello";
String upper = str.toUpperCase(); // 返回"HELLO" -
trim(): 去除首尾空白字符
String str = " Hello ";
String trimmed = str.trim(); // 返回"Hello" -
strip() (Java 11+): 去除首尾空白字符(支持Unicode空白)
String str = " Hello ";
String stripped = str.strip(); // 返回"Hello"
3. char[]和String的转换
3.1 String转char[]
String str = "Hello";
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
// chars = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}
3.2 char[]转String
// 方式1:使用构造函数
char[] chars = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
String str1 = new String(chars);
// str1 = "Hello"
// 方式2:使用构造函数并指定范围
char[] chars = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', 'W', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd'};
String str2 = new String(chars, 0, 5);
// str2 = "Hello"
// 方式3:使用valueOf方法
String str3 = String.valueOf(chars);
// str3 = "Hello"
4. StringBuilder和StringBuffer
由于String是不可变的,频繁的字符串拼接会创建多个对象,影响性能。可以使用StringBuilder(非线程安全)或StringBuffer(线程安全)进行高效的字符串操作。
// 使用StringBuilder
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Hello");
sb.append(" ");
sb.append("World");
String result = sb.toString(); // 返回"Hello World"
// 常用方法
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Hello");
sb.insert(5, " Java"); // 插入字符串,结果为"Hello Java"
sb.delete(5, 6); // 删除指定范围的字符,结果为"HelloJava",左闭右开
sb.reverse(); // 反转字符串,结果为"avaJolleH"
sb.setCharAt(0, 'J'); // 设置指定位置的字符,结果为"JvaJolleH"
sb.replace(1, 4, "a"); // 替换指定范围的字符串,结果为"JaJolleH"
5. 字符串的其他常用操作
5.1 字符串拼接
// 使用+运算符(底层会转换为StringBuilder)
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = s1 + " World"; // 返回"Hello World"
// 使用concat方法
String s3 = s1.concat(" World"); // 返回"Hello World"
// 使用join方法(Java 8+)
String joined = String.join(", ", "apple", "banana", "orange"); // 返回"apple, banana, orange"
5.2 字符串格式化
// 使用format方法
String formatted = String.format("Name: %s, Age: %d", "John", 25); // 返回"Name: John, Age: 25"
// 常用格式说明符
// %s - 字符串,%d - 整数,%f - 浮点数,%c - 字符,%b - 布尔值
String num = String.format("%.2f", 3.14159); // 返回"3.14"
5.3 字符串处理实例
// 字符串反转
public static String reverse(String str) {
return new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString();
}
// 判断回文字符串
public static boolean isPalindrome(String str) {
int left = 0;
int right = str.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (str.charAt(left) != str.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
// 统计字符出现次数
public static int countChar(String str, char ch) {
int count = 0;
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
if (c == ch) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
二、输入输出
1. Scanner 类的基本用法
Scanner 是 Java 中最常用的输入工具类,用于从标准输入、文件或字符串中读取数据。
import java.util.Scanner;
// 创建 Scanner 对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
2. 基本数据类型的读取
2.1 整数类型
// 读取整数
int num = sc.nextInt();
// 读取长整型
long bigNum = sc.nextLong();
// 读取短整型
short smallNum = sc.nextShort();
// 读取字节
byte b = sc.nextByte();
2.2 浮点数类型
// 读取单精度浮点数
float f = sc.nextFloat();
// 读取双精度浮点数
double d = sc.nextDouble();
2.3 字符和字符串
// 读取单个字符
char c = sc.next().charAt(0);
// 读取字符串(以空格为分隔符)
String str = sc.next();
// 读取整行字符串
String line = sc.nextLine();
3. 判断输入是否有效
// 判断是否还有下一个整数
while (sc.hasNextInt()) {
int num = sc.nextInt();
}
// 判断是否还有下一个字符串
while (sc.hasNext()) {
String str = sc.next();
}
// 判断是否还有下一行
while (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
}
// 判断是否还有下一个双精度浮点数
while (sc.hasNextDouble()) {
double d = sc.nextDouble();
}
4. 常见输入模式
4.1 单行输入
// 读取一行数字,以空格分隔
String[] nums = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
for (String num : nums) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(num);
}
// 读取一行数字,以逗号分隔
String[] nums = sc.nextLine().split(",");
for (String num : nums) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(num);
}
4.2 多行输入
// 读取多行,直到遇到空行
while (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
if (line.isEmpty()) break;
// 处理每一行
}
// 读取多行,直到遇到特定值
while (true) {
int num = sc.nextInt();
if (num == 0) break;
// 处理每个数字
}
5. 输出格式控制
// 基本输出
System.out.println("Hello"); // 输出并换行
System.out.print("Hello"); // 输出不换行
System.out.printf("Hello"); // 格式化输出
// 格式化输出示例
int num = 42;
double pi = 3.14159;
System.out.printf("数字:%d,圆周率:%.2f%n", num, pi);
// 输出:数字:42,圆周率:3.14
// 常用格式说明符
// %d - 整数
// %f - 浮点数
// %s - 字符串
// %c - 字符
// %b - 布尔值
// %n - 换行符
6. 注意事项
- 混合使用 nextInt() 和 nextLine()
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // 清除换行符
String line = sc.nextLine(); // 正确读取下一行
- 输入缓冲区处理
// 清空输入缓冲区
while (sc.hasNext()) {
sc.next();
}
- 关闭 Scanner
// 使用完毕后关闭
sc.close();
三、A+B(1)
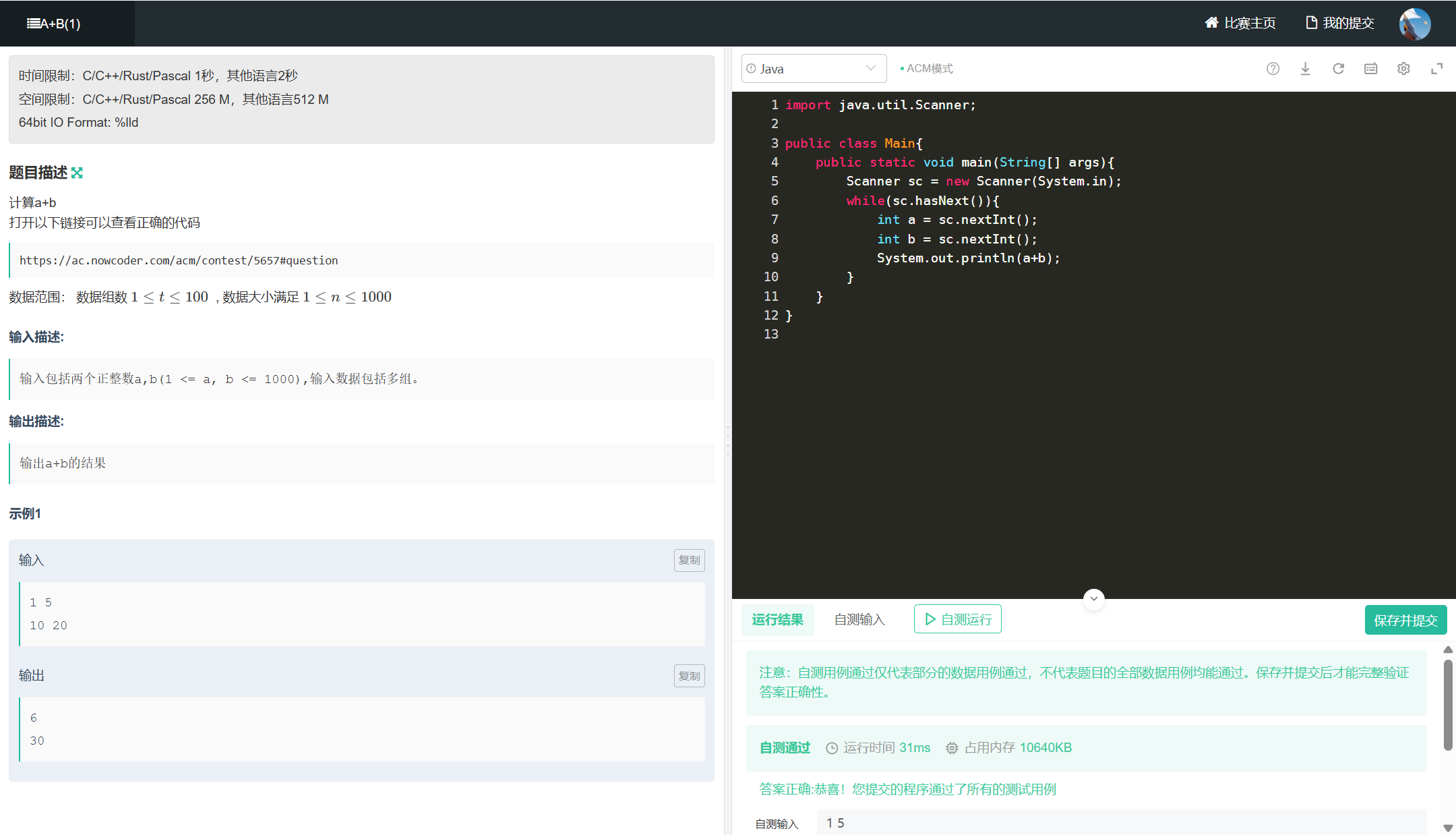
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
}
四、A+B(2)
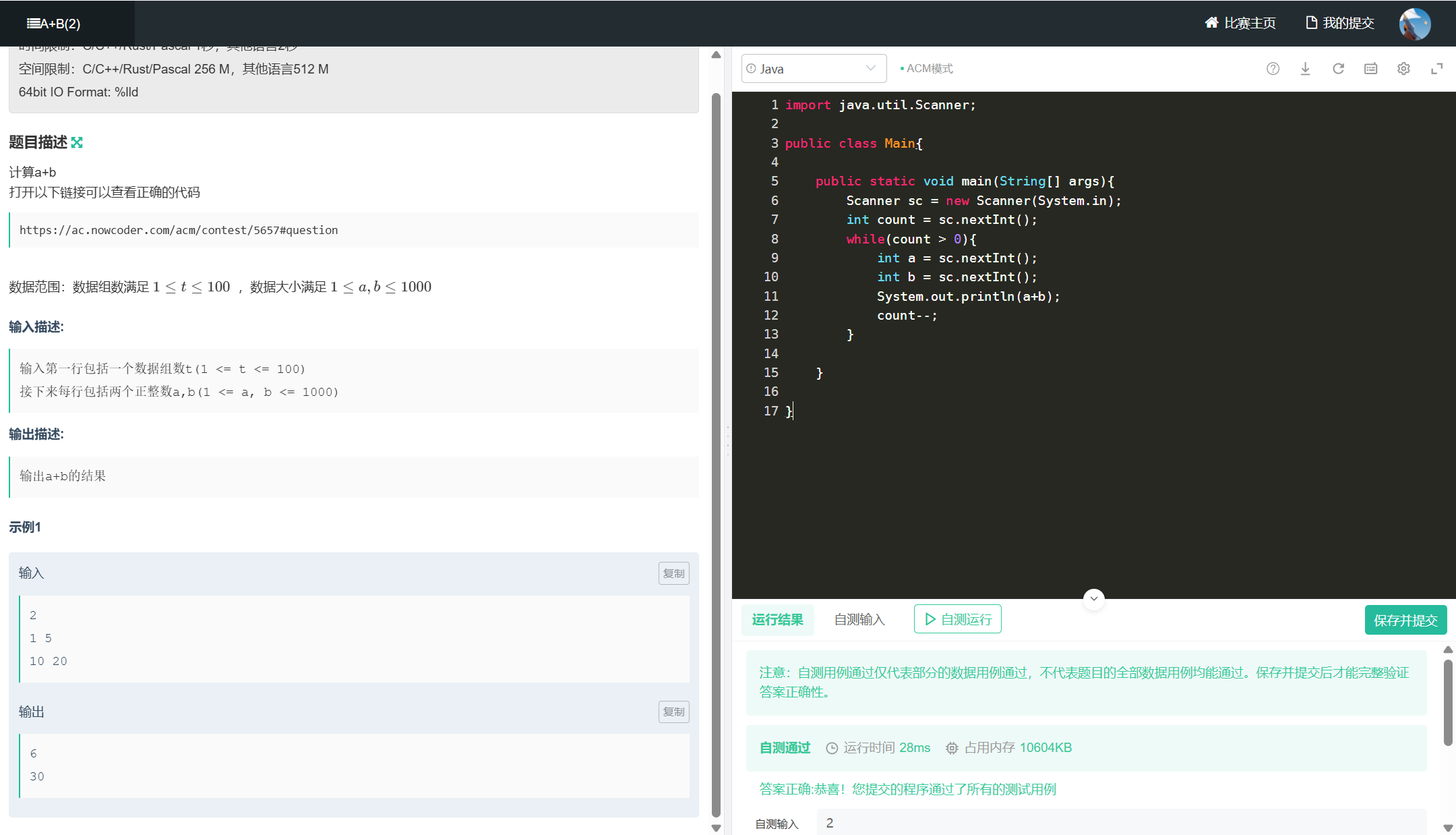
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = sc.nextInt();
while(count > 0){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
count--;
}
}
}
五、A+B(3)
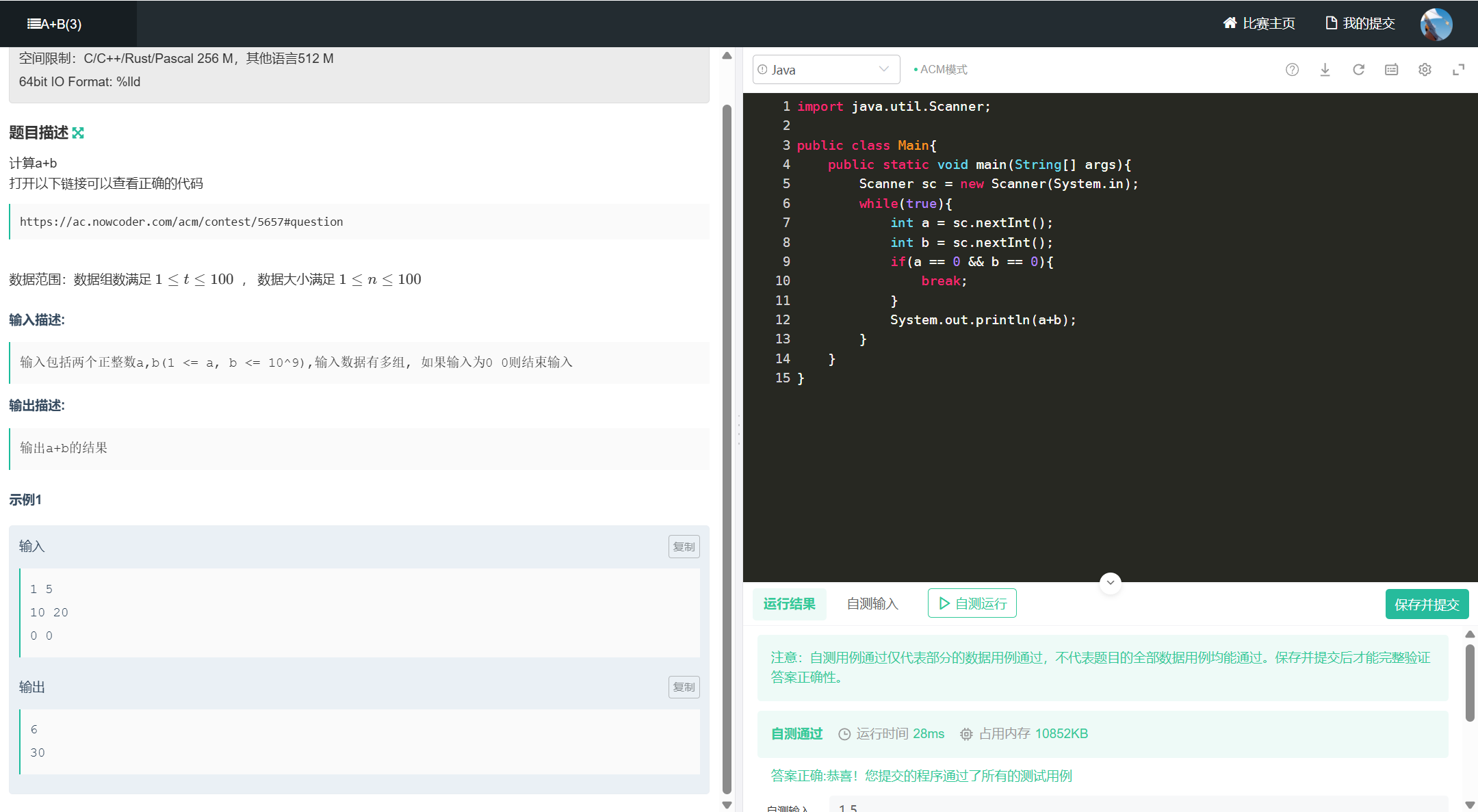
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
if(a == 0 && b == 0){
break;
}
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
}
六、A+B(4)
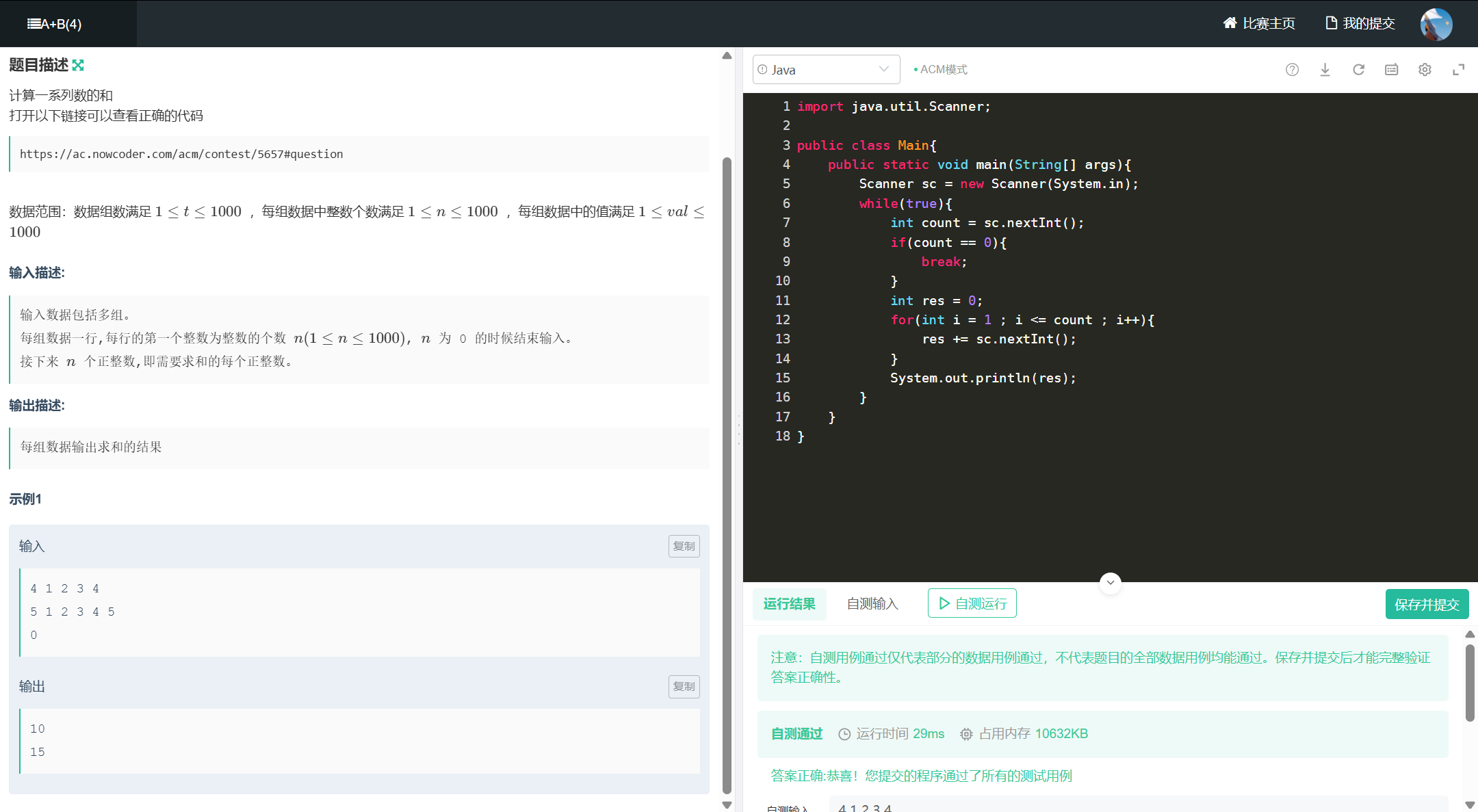
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
int count = sc.nextInt();
if(count == 0){
break;
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= count ; i++){
res += sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
七、A+B(5)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= num ; i++){
int count = sc.nextInt();
int res = 0;
for(int j = 1 ; j <= count ;j++){
res += sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
八、A+B(6)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextInt()){
int count = sc.nextInt();
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= count ;i++){
res += sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
九、A+B(7)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine()){
String[] array = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
int res = 0;
for(String s : array){
res += Integer.valueOf(s);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
十、字符串排序(1)
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = sc.nextInt();
//这行代码 sc.nextLine(); 的作用是:
//清除输入缓冲区中由 sc.nextInt() 留下的换行符,避免影响后续的 sc.nextLine() 操作。
//它是一个常见的处理方式,尤其是在混合使用 sc.nextInt() 和 sc.nextLine() 时。
//如果不加这行代码,程序可能会出现逻辑错误,比如无法正确读取用户输入的字符串数据。
sc.nextLine();
String[] array = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
Arrays.sort(array);
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.length ; i++){
System.out.print(array[i]);
if(i < array.length - 1){
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
}
十一、字符串排序(2)
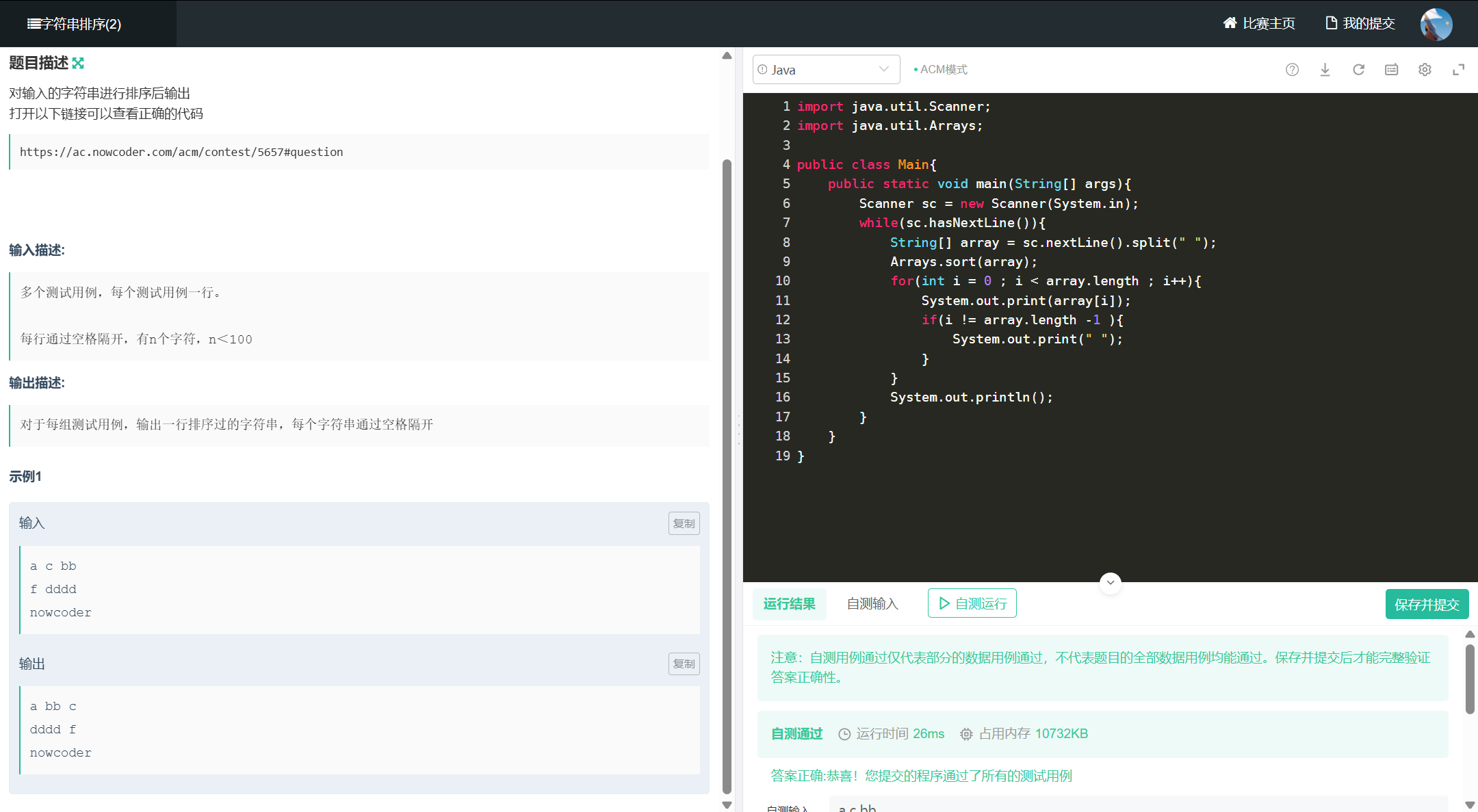
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine()){
String[] array = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
Arrays.sort(array);
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.length ; i++){
System.out.print(array[i]);
if(i != array.length -1 ){
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
十二、字符串排序
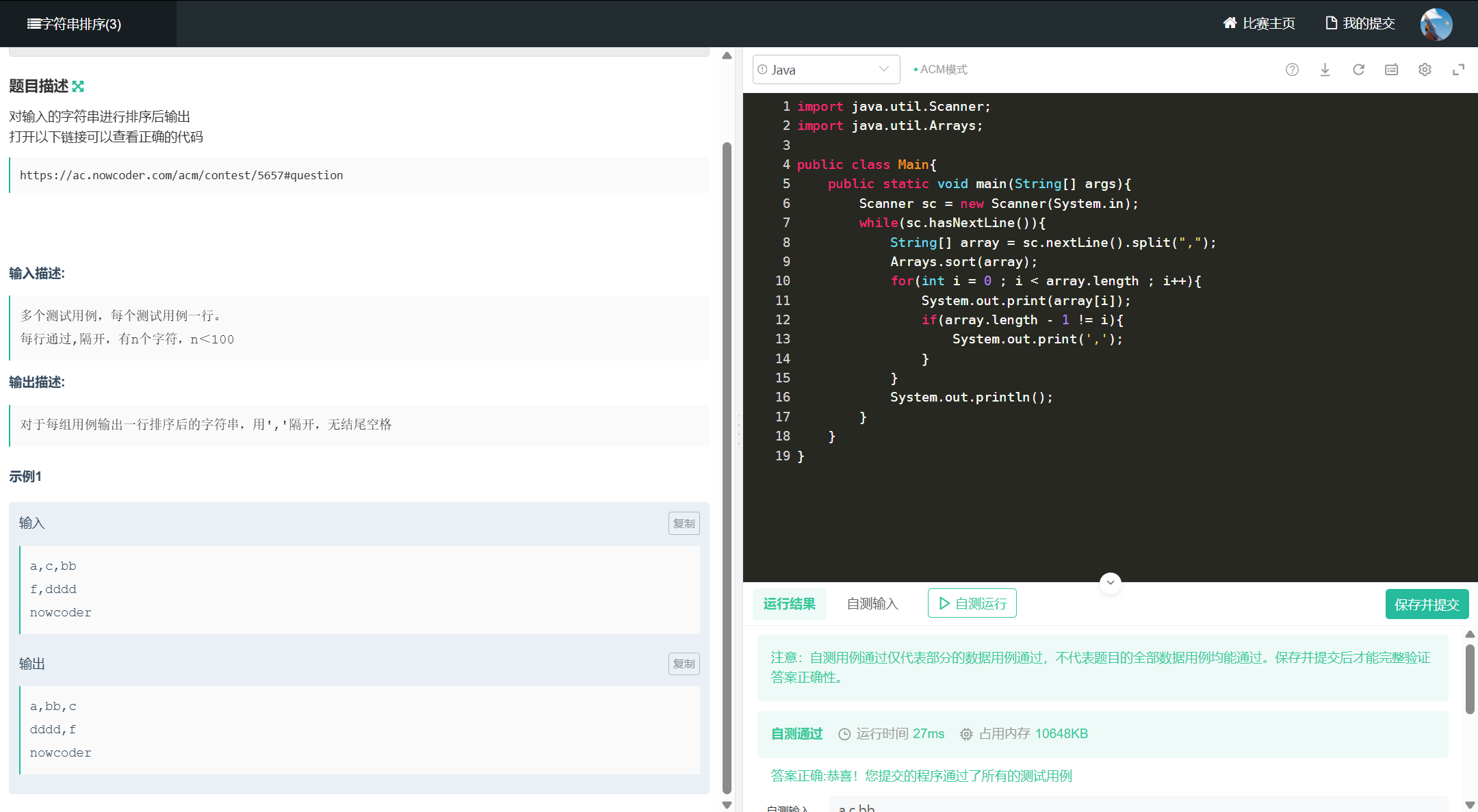
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine()){
String[] array = sc.nextLine().split(",");
Arrays.sort(array);
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.length ; i++){
System.out.print(array[i]);
if(array.length - 1 != i){
System.out.print(',');
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}